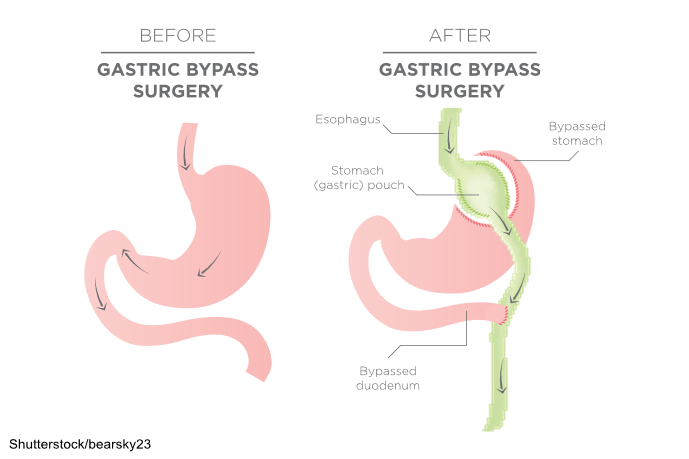
This course reviews the incidence of obesity in the United States and discusses the benefits and risks of various bariatric surgical options. Additionally, the course will examine the criteria for bariatric surgery clearance and discuss preoperative and postoperative care, as well as complications and short- and long-term effects for patients undergoing bariatric surgery.
...purchase below to continue the course
reduced appetite and improved satiety through changes to gut hormonesoverall maintenance that is typically greater than 50% of the weight initially lost (ASMBS, 2021; Lim, 2025a, 2025c; Mitchell et al., 2024; NIDDK, 2020a)
Disadvantages of the gastric bypass procedure include:
- procedural complexity and associated complications
- long-term vitamin and mineral deficiencies, including iron, calcium, folate, and B12
- longer recovery time and hospital stay than other weight-loss procedures
- strict dietary adherence is required for the remainder of their life, including vitamin and mineral supplementation
- follow-up for compliance with dietary adherence (ASMBS, 2021; Lim, 2025a, 2025c; Mitchell et al., 2024; NIDDK, 2020a)
Sleeve Gastrectomy
Sleeve gastrectomy is completed laparoscopically and removes approximately 80% of the stomach. The remaining stomach is tubular in shape, resembling a banana. With a limited stomach size, the amount of food that can be consumed is considerably decreased, thereby prompting weight loss. Hormonal changes are also triggered to aid in weight loss and help reverse some of the associated complications of obesity, including hypertension, cardiac disease, and blood sugar control. This procedure is not reversible. Sleeve gastrectomy was initially offered to patients with severe obesity. However, since sleeve gastrectomy is easier to perform than the Roux-en-Y gastric bypass, it is being performed more commonly across the United States (ASMBS, 2021; Lim, 2025a; NIDDK, 2020a; Rosenthal et al., 2024; Seeras, Sankararaman, et al., 2023). The surgical process of a sleeve gastrectomy is demonstrated in Figure 2.
Figure 2
Sleeve Gastrectomy
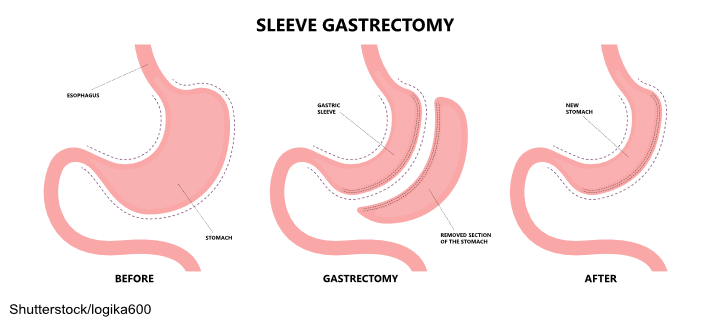
Advantages of the sleeve gastrectomy procedure include:
- rapid and substantial weight loss similar to the Roux-en-Y gastric bypass
- weight-loss maintenance is typically greater than 50% of the initial weight over 3 to 5 years and comparable to Roux-en-Y gastric bypass maintenance
- no bypass of the food stream (as in the Roux-en-Y gastric bypass) and no foreign object (as in the adjustable gastric band)
- short recuperation and hospital stay (typically 2 days)
- changes in gut hormones improve satiety, decrease appetite, and suppress hunger (ASMBS, 2021; Lim, 2025a; NIDDK, 2020a; Rosenthal et al., 2024; Seeras, Sankararaman, et al., 2023)
Disadvantages of the sleeve gastrectomy procedure include:
- nonreversible surgery
- a higher early complication rate than the adjustable gastric band
- potential for long-term vitamin deficiencies (ASMBS, 2021; Lim, 2025a; NIDDK, 2020a; Rosenthal et al., 2024; Seeras, Sankararaman, et al., 2023)
Adjustable Gastric Band
The adjustable gastric band—also known as a lap band or “the band”—utilizes an inflatable band placed around the upper portion of the stomach to create a small pouch above the band, leaving the residual stomach below the band. The device limits the amount of food that can be ingested. The pouch becomes full quickly, and hunger is satisfied. The pouch size can be adjusted by filling the band with sterile saline injected via a port placed under the skin. The pouch size decreases over time with repeated injections into the port. There is no malabsorption of food with this procedure. This procedure can usually be reversed. Due to a high rate of complications or failure, this procedure is rarely done in the United States anymore (ASMBS, 2021; Lim, 2025a; NIDDK, 2020a; Seeras, Acho, et al., 2023). The adjustable gastric band procedure is shown in Figure 3.
Figure 3
Gastric Banding
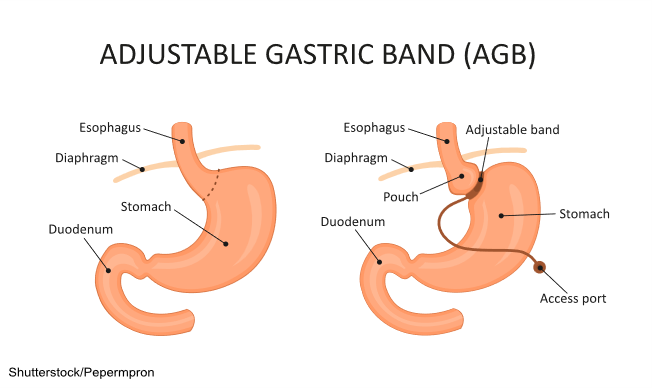
Advantages of the adjustable gastric band procedure include:
- weight loss of 40% to 50% of EBW, which, while less than other procedures, is significant for most individuals
- no incision within the stomach or rerouting of the intestines
- reversible and adjustable
- the lowest rate of early postoperative complications and mortality among all bariatric procedures
- the lowest risk of vitamin or mineral deficiencies of all bariatric procedures (ASMBS, 2021; Lim, 2025a; NIDDK, 2020a; Seeras, Acho, et al., 2023)
Disadvantages of the adjustable gastric band procedure include:
- slower weight loss than other bariatric procedures
- decreased early weight loss compared with other bariatric procedures
- foreign device implantation
- potential for the band to migrate, erode into the stomach, or develop mechanical problems, including tube or port malfunctions
- risk of esophageal dilation (expansion of the tissue), dysmotility (lack of movement), or esophagitis (inflammation) if the patient overeats
- the highest rate of reoperation of all bariatric procedures secondary to complications (ASMBS, 2021; Lim, 2025a; NIDDK, 2020a; Seeras, Acho, et al., 2023)
Biliopancreatic Diversion With Duodenal Switch
A biliopancreatic diversion with duodenal switch is the least common weight-loss surgery discussed in this module. This surgery involves two steps, starting with a sleeve gastrectomy. As described previously, approximately 80% of the stomach is removed, and a banana-shaped tubular stomach is created. The pyloric sphincter also remains, which allows food to pass into the small intestine. The second part of the surgery bypasses most of the small intestine. During this procedure, the duodenum (first portion of the small intestine) is divided just past the pyloric sphincter. The lower portion of the small intestine is then connected to the outlet of the newly created stomach pouch. When the patient eats, food goes through the tubular stomach and empties directly into the lower portion of the small intestine, bypassing about 75% of the small intestine. Consequently, food does not mix with the natural pancreatic enzymes or bile until it reaches a later stage in the small intestine, resulting in decreased nutrient and calorie absorption (ASMBS, 2021; Conner & Nottingham, 2022; Lim, 2025a; NIDDK, 2020a). This procedure is depicted in Figure 4.
Figure 4
Biliopancreatic Diversion
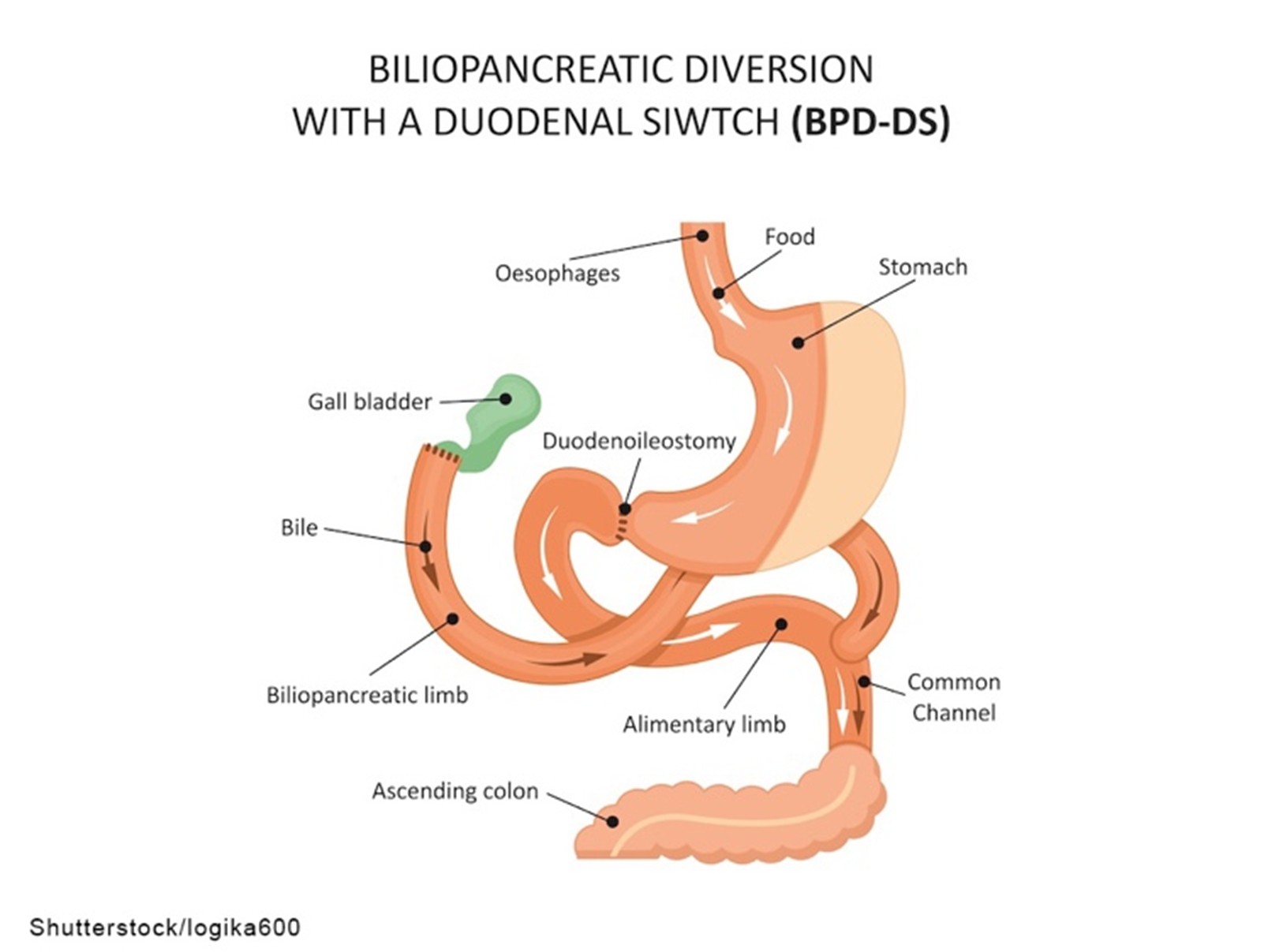
Advantages of the biliopancreatic diversion with duodenal switch procedure include:
- weight loss of 60% to 70% of EBW or higher at the 5-year follow-up, which is higher than with other bariatric surgeries
- potential for patients to eat more “normal” meals after a few months
- enhanced gut hormones to reduce appetite and improve satiety
- most effective at reducing the rate of T2DM in comparison to other bariatric surgeries
- reduced fat absorption (up to 70%) due to delayed pancreatic enzyme activity (ASMBS, 2021; Conner & Nottingham, 2022; Lim, 2025a; NIDDK, 2020a)
Disadvantages of the biliopancreatic diversion with duodenal switch procedure include:
- a higher complication rate and increased mortality risk with this procedure than with other bariatric surgeries
- greater potential for vitamin and mineral deficiencies than with other procedures
- a more extended hospital stay after surgery compared to gastric bypass or gastric band procedures
- compliance with diet and follow-up visits is crucial with this procedure to avoid serious complications from protein and vitamin deficiencies (ASMBS, 2021; Conner & Nottingham, 2022; Lim, 2025a; NIDDK, 2020a)
Benefits and Risks of Bariatric Surgery
Evidence regarding the benefits of weight-loss surgery dates back to the 1960s. The last few decades have seen a significant rise in weight-loss surgeries as an increase in obesity has occurred. Numerous studies have found that all bariatric procedures offer better long-term weight management outcomes than nonsurgical weight-loss options, such as diet and exercise, or other supportive services (e.g., weight-loss programs). Compared to conventional weight-loss methods, there is a decreased risk of mortality and morbidity for patients with severe obesity after bariatric surgery. In addition, the weight loss associated with bariatric surgery leads to reduced rates of OSA, osteoarthritis, stress incontinence, dyslipidemia, hypertension, coronary artery disease, acute cardiovascular events, T2DM, obesity-related cancers, and death. For individuals with severe obesity, weight-loss surgery can extend their life by years (ASMBS, 2020, 2021; Crossan & Sheer, 2023b; Levy & Nessen, 2025; NIDDK, 2020b).
The risks associated with bariatric surgeries can include complications related to general anesthesia. Immediate postoperative complications include bleeding, infection, diarrhea, deep venous thrombosis (DVT), bowel obstruction, and perforation. Long-term complications may include ulcerations from the gastric band or nutritional deficits resulting from the lack of absorption associated with all bariatric procedures. Nutrient deficiencies can lead to anemia and osteoporosis. Rapid weight loss can also increase the risk of gallstones because it can alter the balance of cholesterol, lecithin, and bile acids, preventing the gallbladder from emptying adequately. Although not specifically a risk of surgery, patients who undergo bariatric surgery will need to follow long-term dietary modifications, including limiting carbohydrates, eating small meals, and refraining from alcohol (ASMBS, 2020, 2021; Crossan & Sheer, 2023b; Levy & Nessen, 2025; NIDDK, 2020c).
Criteria for Bariatric Surgery Clearance
Bariatric surgery is not recommended for all patients and can be costly. Patients considering bariatric surgery should be counseled to contact their health insurance company directly to determine coverage and discuss payment options with their HCP’s billing department for any costs not covered by their health insurance. Furthermore, the physical, mental, and social aspects of the surgery require HCPs to conduct extensive screening processes to clear a patient for the procedure. Generally, these procedures are considered for anyone with a BMI over 40 or a BMI between 35 and 39, along with comorbidities such as severe OSA, hypertension, T2DM, or other serious weight-related health problems. Occasionally, a patient with a BMI between 30 and 34 may be considered if they have serious weight-related health problems. Candidate approval for bariatric surgery should be based on prior weight-loss attempts, the presence and severity of comorbidities, overall health status for surgery consideration, and the ability to comply with preoperative and postoperative instructions. A comprehensive assessment, focusing on comorbidities such as cardiac and respiratory concerns, can create a safer environment for intraoperative care. In addition, closer postsurgical monitoring may be required for those with identified risks before surgery (ASMBS, 2021; Lim, 2025b; Sall & Jones, 2023).
Medical clearance for bariatric surgery should include a thorough history that explores the patient’s weight history, dietary history, social history, psychological history (particularly eating disorders, physical abuse, or substance use), physical activity, review of medications, and psychosocial behaviors/factors that might impact weight loss or future success due to nonadherence. The clinical examination should include assessments of laboratory values, including electrolytes, vitamins, iron, folate, calcium, a basic metabolic panel (BMP), a complete blood count (CBC), and a lipid profile. Serum albumin and prealbumin should also be checked since they are indicators of overall nutritional status. Patients with T2DM should achieve glycemic control before surgery, thereby decreasing their risk of postoperative complications (Lim, 2025b; Sall & Jones, 2023).
Since cardiac complications often coexist with obesity, stabilizing all comorbidities before surgery is vital to prevent postoperative complications. All patients evaluated for bariatric surgery should have a 12-lead electrocardiogram (ECG), followed by a cardiac stress test, either with a treadmill or with scintigraphic imaging. These may not be possible for patients with severe obesity due to the weight limitations of testing equipment, difficulty in accurately interpreting images due to body habitus, and each patient’s physical capabilities. For these patients, pharmacological stress testing may be done with or without ultrasound contrast agents to determine cardiac function as accurately as possible (Lim, 2025b; Sall & Jones, 2023).
Airway complications are prevalent in patients with severe obesity due to mechanical restriction. Preoperative pulmonary function testing may help identify patients at high risk for pulmonary complications following the surgery. Screening tools such as the STOP-BANG (snoring, tired, observed, pressure, BMI, age, neck size, and gender) or Berlin score are available to help identify patients at risk for OSA. Patients who are identified as at risk for OSA during this preoperative testing should be referred for evaluation with overnight polysomnography (sleep study) and may need to begin treatment with a continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) machine during sleep. Patients who present with daytime hypercapnia, also known as obesity hypoventilation syndrome (OHS), may also benefit from CPAP therapy or bi-level positive pressure (Bi-PAP) preoperatively. Routine spirometry testing may be performed for individuals with a high risk of pulmonary complications, and preoperative optimization with a pulmonologist may be warranted to improve patient outcomes during and after surgery (Kline, 2025; Lim, 2025b; Olson et al., 2025; Sall & Jones, 2023).
Preoperative psychological evaluation and clearance are essential to a patient’s success after surgery. The long-term outcomes of surgery depend on each patient’s ability to adhere to a strict postoperative diet and lifestyle regimen. This evaluation will also prepare the patient for possible emotional adjustments as their weight is reduced. A comprehensive behavioral assessment should include a history of any eating or behavioral disorders, any current or history of anxiety or mood disorders, all current or past mental health conditions or treatments, and an evaluation of the patient’s motivation for weight loss. Perhaps more important than the physical ability to withstand bariatric surgery is the patient’s psychological capacity to learn, comply, and adapt to the changes that will occur during the perioperative cycle. Social support systems should be identified during the psychological evaluation, as the best outcomes involve the presence of family members, friends, and a community that supports the patient’s weight-loss journey with bariatric surgery. This evaluation will also identify barriers to postoperative success through a lack of social or emotional support in these areas (Lim, 2025b; Sall & Jones, 2023).
A registered dietitian (RD) should complete a nutritional evaluation. This assessment will focus on preoperative weight-loss efforts, a nutritional assessment of current eating behaviors, and education on postoperative eating behaviors that must be strictly followed. Although some controversy exists regarding the need for preoperative weight loss for long-term success, studies indicate that preoperative nutritional counseling is crucial to achieving postoperative dietary compliance. A careful evaluation of micronutrient and macronutrient measurements should be completed during the nutritional assessment. A nutritionist or RD should educate the patient on the postoperative diet components before all bariatric surgical procedures. However, for patients undergoing a malabsorptive bariatric procedure, such as the gastric bypass or the biliopancreatic diversion with duodenal switch, a more extensive perioperative nutritional evaluation should be conducted to offset anticipated deficiencies, as the portion of the intestines removed allows for the most efficient absorption of vitamins and minerals. These patients may have deficiencies in iron, calcium, magnesium, and vitamins, including vitamin B12 (Herron & Herrington, 2025; Lim, 2025b; Sall & Jones, 2023).
Preoperative gastrointestinal (GI) imaging or an upper GI radiographic series should be completed to pinpoint any preexisting anatomical or physiological abnormalities. As the GI tract will be modified during bariatric surgery, this provides a preoperative view of the esophagus and gastric anatomy, including esophageal clearance and the presence or size of a hiatal hernia. In addition, an abdominal ultrasound is recommended to assess for biliary tract pathology. If undiagnosed cholelithiasis is present, the rapid weight loss induced by bariatric surgery can provoke existing gallstones to become symptomatic. The ultrasound should also assess for steatosis (abnormal retention of fat), fibrosis (abnormal accumulation of scar tissue), or the presence of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (inflammation accompanied by concurrent fat accumulation) in the liver. Esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD) should be performed as part of the preoperative evaluation for a bariatric surgical candidate. The pharynx, esophagus, stomach, and duodenum are evaluated using a flexible endoscope. This procedure can rule out any underlying GI disease, severe esophagitis, Barrett’s esophagus, or malignancy of the upper GI tract (Lim, 2025b; Sall & Jones, 2023).
While there is controversy over preoperative weight-loss requirements, some studies show that patients with a preoperative weight-loss requirement have a higher percentage of excess weight loss (EWL) at 6 months post surgery. The health care team will determine the individual goals of each bariatric patient before surgery. One advantage of preoperative weight loss is that it reduces abdominal fat and liver volume, thereby improving access to the stomach during laparoscopic procedures and shortening operative time. There is evidence that a low (800 to 1200 kcal) or very low (400 to 800 kcal) calorie diet for 2 to 12 weeks can lead to weight loss and a 15% to 30% reduction in liver volume, thereby increasing the ease of bariatric surgery. However, the inability to complete this type of diet or lose weight should not preclude someone from receiving bariatric surgery (Lim, 2025b; Sall & Jones, 2023).
The major contraindications to bariatric surgery are psychological features that might amplify the impact of the surgery, or physical conditions or comorbidities that put a patient at extremely high risk for complications, such as cardiac or other conditions. However, most patients benefit from the procedure and subsequent weight loss, making their clearance for surgery likely (Lim, 2025b; Sall & Jones, 2023). Refer to Table 1 for the preoperative checklist recommended for all bariatric surgery procedures in the 2019 updated clinical practice guidelines.
Table 1
Preoperative Checklist for Bariatric Surgery
Assessment | Component |
- Complete history and physical
| - Obesity-related comorbidities
- Causes of obesity
- Weight/BMI
- Weight-loss history
- Commitment
- Contraindications due to surgical risk
|
| - Fasting blood glucose
- Lipid panel
- Kidney function
- Liver profile
- Urine analysis
- Prothrombin time/INR
- Blood type
- CBC
|
| - Iron studies
- Vitamin B12
- Folic acid (red blood cell folate, homocysteine, methylmalonic acid, optional)
- 25-vitamin D (vitamins A and E optional)
- Consider more extensive testing for patients undergoing malabsorptive procedures
|
- Cardiopulmonary evaluation with sleep screening
| - ECG
- Chest radiograph
- Echocardiogram if cardiac disease or pulmonary hypertension is suspected
- DVT evaluation, if clinically indicated
|
| - H. pylori screening in high-prevalence areas
- Gallbladder evaluation, if clinically indicated
|
| - Hemoglobin A1C with suspected or prediagnosed T2DM or prediabetes
- Optimized glycemic control
- Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) with symptoms or increased risk of thyroid disease
- Androgens with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) suspicion (total/bioavailable testosterone, dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate [DHEAS])
- Screening for Cushing’s syndrome, if clinically indicated
|
- Nutrition evaluation by an RD
| - Review postoperative bariatric diet, including what, how, and when to eat and what foods to avoid
|
- Psychosocial–behavioral evaluation
| - Evaluate the commitment to bariatric surgery
- Screen for untreated psychiatric disorders, dangerous eating habits, or poor coping skills
|
- Documented medical necessity for bariatric surgery
| - Determine that the patient is a candidate for bariatric surgery
|
| - Review benefits and risks
- Signed consent in the chart
|
- Relevant financial information
| - Evaluate insurance coverage and potential out-of-pocket expenses
|
- Continued preoperative weight-loss surgery efforts
| - Evaluate the patient for presurgery diet and weight-loss success
|
| - Pregnancy should be avoided preprocedure and for 12 to 18 months after surgery
- Patients who become pregnant after bariatric surgery should be monitored for appropriate weight gain, nutritional supplementation, and fetal health
|
- Smoking cessation counseling
| - Review the risks of smoking and offer smoking cessation tools
|
- Verify cancer screening by the primary care provider (PCP)
| - Screening for obesity-related cancer is recommended before bariatric surgery
|
(Lim, 2025b; Mechanick et al., 2020; Sall & Jones, 2023)
Perioperative Care for Bariatric Patients
Preoperative Nursing Care
Nurses should discuss postsurgical weight-loss goals. Each patient and their health care team should develop goals tailored to the patient’s specific situation and willingness to comply with future restrictions (ASMBS, 2021; Lim, 2024c, 2025b). Nurses should focus on the following during preoperative care:
- Patient care needs:
- identify individual physical risk factors and develop a plan to offset any anticipated risk
- develop relationships with the health care team to improve adherence post surgery
- discuss the strengths and weaknesses of the patient and their support system (ASMBS, 2021; Lim, 2024c, 2025b)
- Education topics:
- the specific procedure to be performed and the associated risks
- discharge planning for surgery
- the importance of dietary compliance and follow-up with HCPs
- what and how much food can be eaten after surgery
- understanding the connection between food and triggers to overeating and behavioral changes that can lead to a healthier lifestyle
- the importance of exercise to prepare mentally and physically for surgery and continuation after surgery (ASMBS, 2021; Lim, 2024c, 2025b)
Postoperative Nursing Care
Patient care focuses on maintaining respiratory and cardiac function, managing pain, and recognizing surgical complications early during surgery and in the postoperative period. During the early postoperative period, nurses should prioritize each patient’s pain management, safety, and hydration. Patient care needs should include the following:
- maintenance of airway/breathing through the use of incentive spirometry or other respiratory therapies
- continuous monitoring of vital signs
- administration of intravenous (IV) fluids and any other ordered medications
- regular monitoring for bleeding
- pain management
- venous thromboembolism event (VTE) prophylaxis (ASMBS, 2021; Hamad, 2025; Seelbach & D'Almeida, 2022)
Refer to Table 2 for details on early postoperative care outlined in the 2019 updated clinical practice guidelines.
Table 2
Early Postoperative Care
| Gastric Band | Gastric Sleeve | Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass | Biliopancreatic diversion |
Monitored telemetry for 24 hours if high risk for MI | X | X | X | X |
Protocol-derived staged meal progression supervised by RD | X | X | X | X |
Healthy eating education by an RD | X | X | X | X |
Calcium citrate 1200–1500 mg/day | X | X | X |
|
Multivitamin plus minerals (tabs for minimum requirement) | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
Vitamin D, at least 3000 units/day, titrate to >30 ng/mL | X | X | X | X |
Vitamin B12 as needed to achieve the normal range | X | X | X | X |
Adequate hydration (>1.5 L/d PO) | X | X | X | X |
Blood glucose monitoring with diabetes or hypoglycemic symptoms | X | X | X | X |
Pulmonary hygiene, spirometry, DVT prophylaxis, including Thrombo-Embolic Deterrent (TED) hose and sequential circulatory devices (SCDs) | X | X | X | X |
If unstable, consider pulmonary embolus (PE), intestinal leak | PE | PE | PE/IL | PE/IL |
If rhabdomyolysis (breakdown of damaged skeletal muscle) is suspected, check creatine phosphokinase (CPK) | X | X | X | X |
(Mechanick et al., 2020)
Nurses should provide postoperative patient education on:
- reporting pain to the nurse before it becomes severe and taking pain medication routinely and as needed during the immediate postoperative period
- early ambulation to decrease complications and asking for assistance before getting out of bed to avoid injury
- using an incentive spirometer and other respiratory treatments to avoid postoperative pneumonia
- maintaining nothing by mouth (NPO) initially, followed by a gradual dietary introduction of liquids, progressing to a pureed diet
- the postoperative medication regimen (Hamad, 2025; Mechanick et al., 2020; Seelbach & D'Almeida, 2022)
Nurses should provide dietary education for bariatric surgery patients in the early days after surgery. Important education points should consist of the following (Hamad, 2025; Herron & Herrington, 2025; Mechanick et al., 2020; Seelbach & D'Almeida, 2022):
- Start with a clear liquid diet before progressing to thicker liquids.
- After 2 weeks, start a blended, pureed diet. Liquid supplements or powders can meet the protein requirements during this period.
- Eat small meals every 2 hours.
- Foods should be high in protein and low in carbohydrates, calories, fat, and sugar.
- Fluids should be consumed between meals, with a goal of 1 cup of fluids between each small meal, 6 to 8 times per day, for a total of 64 ounces of fluids daily.
- Maintain a log of all food consumed and protein intake, with a protein goal of 65 to 75 grams daily post surgery (this may take some time to achieve).
- Chew food thoroughly and take small bites.
- Do not use straws or chew ice, as this introduces air into the stomach, which can cause pain.
- Caloric intake for the first 2 months should remain around 300 to 600 calories per day, focusing on thin and thicker liquids, not exceeding 1000 calories.
- Avoid rice, bread, raw vegetables, fresh fruits, and carbonated or sugary beverages.
- Avoid pork or steak that is difficult to chew; ground meats are a good alternative.
- Avoid alcohol, as this is absorbed more rapidly and can cause an increased effect on blood alcohol levels.
- Liquid vitamin supplements are best. Others should be crushed or cut into small pieces.
- A multivitamin with selenium, copper, zinc, 400 mcg of folic acid, and 18 mg of iron is advised. Take two tablets daily for at least 3 months after surgery, followed by one tablet daily for the remainder of your life.
- Take a calcium supplement with 1200 to 2000 mg daily.
- Take a vitamin D supplement with 800 to 1000 IU daily.
- Take an oral or sublingual vitamin B complex supplement containing 500 mcg of vitamin B daily.
Complications of Bariatric Surgery
Since most bariatric procedures are performed laparoscopically, the surgical risk is lower than with traditional open abdominal surgeries, including wound infections and delayed healing. However, the risk involved with general anesthesia and rerouting of the GI tract is unchanged. The most common postsurgical risks include VTE, bleeding, and bowel obstruction. Anesthesia risks are a concern with any surgery, but this risk increases for patients with severe obesity. However, improved anesthesia and surgical management have decreased this risk, and appropriate cardiac and pulmonary function testing during the preoperative evaluation for bariatric surgery can reduce it even further (Hamad, 2025; Lim, 2024b; Seelbach & D'Almeida, 2022).
The risk of blood clots or VTE is a primary concern postoperatively for patients with severe obesity. Early ambulation after surgery is the most effective method for preventing VTE. Mechanical and pharmacological prophylaxis should also be ordered, including lower extremity compression stockings (TEDs), SCDs, and pharmacologic prophylaxis. The use of low-molecular-weight heparin is recommended for bariatric patients, such as enoxaparin (Lovenox), fondaparinux (Arixtra), or dalteparin (Fragmin), over unfractionated heparin (Heparin sodium). Evidence has shown a decrease in VTE with the use of low-molecular-weight heparin, with no increase in postoperative bleeding rates among this group. However, bleeding precautions should be implemented, and nurses should monitor for bruising or bleeding and avoid invasive procedures. Bleeding related to the surgery is possible but rare. Most facilities perform a postoperative upper GI series to rule out bleeding or leakage in patients undergoing gastric bypass, sleeve gastrectomy, and biliopancreatic diversion with duodenal switch procedures. Symptoms indicating bleeding could include hematemesis, severe left upper quadrant pain, back and shoulder pain, intractable hiccups, severe nausea with retching, and melena. For a suspected bleed, nurses should contact an HCP immediately (Hamad, 2025; Lim, 2024b; Seelbach & D'Almeida, 2022).
Bowel obstruction is an unlikely but potentially serious complication of bariatric surgery. This complication is often associated with the gastric bypass procedure, but it can also occur with other procedures. The obstruction can be related to adhesions, internal hernia, intussusception (when one section of the intestine telescopes inside another, causing a blockage), and intraluminal clots or strictures. In addition, there may be defects in the mesentery of the bowel that lead to an obstruction. These patients typically report severe abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting. The abdomen will typically be tender to palpation but without rebound tenderness. A patient with intussusception may present with currant jelly stools, an abdominal mass, or peritonitis. Regardless of the cause, surgical intervention is typically required to correct this condition (Hamad, 2025; Lim, 2024b; Seelbach & D'Almeida, 2022).
Bariatric Surgery Short- and Long-Term Effects
The most significant impact of bariatric surgery, both in the long and short term, is weight loss. Weight loss can lead to increased activity, improved overall health, and greater self-esteem. More than 90% of individuals who undergo weight-loss surgery maintain 50% of their EWL after surgery, and more than 80% maintain over 50% of their EWL after surgery, indicating long-term success with these procedures. Population-based studies involving individuals with obesity have demonstrated that those undergoing bariatric surgery have a lower risk of mortality than their counterparts who do not have surgery. One study demonstrated an 89% reduction in mortality over 5 years for patients who chose to undergo bariatric surgery compared to those who did not (ASMBS, 2020, 2021; Telem et al., 2025). In addition, improvement in the following coexisting diseases has been found across studies:
- hypertension
- T2DM
- OSA
- osteoarthritis
- asthma
- GERD
- NAFLD
- urinary stress incontinence
- venous stasis
- infertility
- hyperlipidemia (ASMBS, 2020, 2021; Telem et al., 2025)
Most patients report improved sleep, the ability to complete activities of daily living, and an overall enhanced quality of life after surgery. Depression, anxiety, and other mental health illnesses often improve as well. Sexual function, relationships, and social interactions often improve, and patients frequently report enhanced employability (ASMBS, 2020, 2021; Telem et al., 2025).
Bariatric Surgery in Adolescents and Children
Children and adolescents are also affected by obesity. Up to 80% of children with obesity will be affected by obesity in adulthood. They are often affected by the same weight-related conditions as adults, including hypertension, OSA, T2DM, and asthma. Additionally, children and adolescents are often bullied or are victims of weight bias, inducing depression and anxiety. While noninvasive treatments such as lifestyle modification, pharmacotherapy, and behavioral therapy are preferred, some cases require more drastic measures, including bariatric surgery. The most common procedures in children and adolescents are Roux-en-Y gastric bypass and sleeve gastrectomy. The goal of bariatric surgery in this population is to provide the most significant benefit with the lowest risk (ASMBS, 2022; Inge, 2025; Skelton & Klish, 2025). The criteria for this age group are:
- BMI 35 or higher with major comorbidities (T2DM, moderate to severe OSA, pseudotumor cerebri, or NAFLD)
- BMI 40 or greater with less severe comorbidities (hypertension, hyperlipidemia, mild or moderate OSA; ASMBS, 2022; Inge, 2025; Skelton & Klish, 2025)
There appear to be short-term benefits to bariatric surgery in this population, with improved depression, quality of life, and fewer eating disturbances. Negative psychosocial risks may exist but are not well documented. Vitamin and nutritional deficiencies may exist, in both the short and long term, and must be closely monitored to ensure proper growth and development during adolescence. Informed consent among children occurs as part of a formal agreement called “assent.” Assent involves each child in the decision-making process and seeks to ensure they agree with the surgery without coercion from their family or medical staff. The clinical team must carefully consider an adolescent’s cognitive, social, and emotional abilities to make decisions. It is optimal to have a supportive family and a willing, committed child on the same page regarding their future health decisions. In situations where this does not exist, the HCP must ensure that all efforts are made to ensure the child’s best interests are considered by all parties involved (ASMBS, 2022; Inge, 2025).
Future Opportunities in Bariatrics
While already in practice with some health care organizations, the intragastric balloon is a more recent weight-loss procedure that does not require surgery. The procedure is an option for those who are overweight/obese when diet and exercise have not been successful. Like bariatric surgeries, a commitment to lose weight is necessary for the intragastric balloon. Patients must adopt a permanent, healthy diet and exercise routine to achieve long-term success with the procedure (Crossan & Sheer, 2023a; Lim, 2024a). This procedure is an option for individuals who have the following:
- a BMI between 30 and 40 who have tried and failed previous attempts at weight management with lifestyle changes
- a willingness to commit to a healthy lifestyle and follow the medical plan, including behavioral therapy
- no previous esophageal or stomach surgeries (Crossan & Sheer, 2023a; Lim, 2024a)
An intragastric balloon can be placed in an outpatient procedure in an endoscopy suite using sedatives and avoiding general anesthesia. This balloon makes patients feel full faster, decreasing the amount of digested food. The balloon also appears to alter the hormones that regulate appetite, thereby improving satiety. The amount of weight loss depends on the corresponding changes in lifestyle habits. The typical weight loss is 6% to 15% of body weight in the first 6 months after placement. For those receiving concurrent behavioral therapy, the average weight loss increases to 29% of their EBW, compared to only 14% of EBW among the group that received behavioral therapy alone. Although intragastric balloons are safe and effective, weight gain can occur after the balloon removal, with only 50% of the patients maintaining a 20% EWL at 1 year and 25% at 5 years after removal. Minor complications for the intragastric balloon include pain and nausea after the insertion that subsides within hours to days and can be treated with oral medications. A serious risk includes balloon deflation, allowing the balloon to move through the digestive system and cause a blockage, which may require surgery to retrieve it. Other potential risks include stomach ulcers or perforations that may require surgical repair. Intragastric balloons are contraindicated in patients with coagulation disorders, pregnancy, active bleeding in the upper GI tract, or severe liver disease (Crossan & Sheer, 2023a; Lim, 2024a).
References
American Society for Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery. (n.d.). Disease of obesity. Retrieved June 26, 2025, from https://asmbs.org/patients/disease-of-obesity
American Society for Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery. (2020). Benefits of metabolic and bariatric surgery. https://asmbs.org/patients/benefits-of-metabolic-and-bariatric-surgery
American Society for Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery. (2021). Bariatric surgery procedures. https://asmbs.org/patients/bariatric-surgery-procedures#bypass
American Society for Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery. (2022). Childhood and adolescent obesity. https://asmbs.org/patients/adolescent-obesity
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2024a). About body mass index (BMI). https://www.cdc.gov/bmi/about/index.html
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2024b). Adult obesity facts. https://www.cdc.gov/obesity/adult-obesity-facts
Conner, J., & Nottingham, J. M. (2022). Biliopancreatic diversion with duodenal switch. StatPearls [Internet]. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK563193
Crossan, K., & Sheer, A. J. (2023a). Intragastric balloon. StatPearls [Internet]. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK578184
Crossan, K., & Sheer, A. J. (2023b). Surgical options in the treatment of severe obesity. StatPearls [Internet]. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK576372
Hamad, G. (2025). Bariatric surgery: Postoperative and long-term management of the uncomplicated patient. UpToDate. Retrieved June 29, 2025, from https://www.uptodate.com/contents/bariatric-surgery-postoperative-and-long-term-management-of-the-uncomplicated-patient
Herron, D. M., & Herrington, H. (2025). Bariatric surgery: Postoperative nutritional management. UpToDate. Retrieved June 29, 2025, from https://www.uptodate.com/contents/bariatric-surgery-postoperative-nutritional-management
Inge, T. H. (2025). Surgical management of severe obesity in adolescents. UpToDate. Retrieved June 30, 2025, from https://www.uptodate.com/contents/surgical-management-of-severe-obesity-in-adolescents
Kline, L. R. (2025). Clinical presentation and diagnosis of obstructive sleep apnea in adults. UpToDate. Retrieved June 29, 2025, from https://www.uptodate.com/contents/clinical-presentation-and-diagnosis-of-obstructive-sleep-apnea-in-adults
Levy, S. M., & Nessen, M. (2025). Metabolic and bariatric surgery. https://www.merckmanuals.com/professional/nutritional-disorders/obesity-and-the-metabolic-syndrome/metabolic-and-bariatric-surgery
Lim, R. B. (2024a). Intragastric balloon therapy for weight loss. UpToDate. https://www.uptodate.com/contents/intragastric-balloon-therapy-for-weight-loss
Lim, R. B. (2024b). Metabolic and bariatric operations: Early morbidity and mortality. UpToDate. Retrieved June 29, 2025, from https://www.uptodate.com/contents/metabolic-and-bariatric-operations-early-morbidity-and-mortality
Lim, R. B. (2024c). Patient education: Weight loss surgery and procedures (Beyond the basics). UpToDate. Retrieved June 29, 2025, from https://www.uptodate.com/contents/weight-loss-surgery-and-procedures-beyond-the-basics
Lim, R. B. (2025a). Bariatric procedures for the management of severe obesity: Descriptions. UpToDate. Retrieved June 26, 2025, from https://www.uptodate.com/contents/bariatric-procedures-for-the-management-of-severe-obesity-descriptions
Lim, R. B. (2025b). Bariatric surgery for management of obesity: Indications and preoperative preparation. UpToDate. Retrieved June 29, 2025, from https://www.uptodate.com/contents/bariatric-surgery-for-management-of-obesity-indications-and-preoperative-preparation
Lim, R. B. (2025c). Laparoscopic Roux-en-Y gastric bypass. UpToDate. Retrieved June 26, 2026, from https://www.uptodate.com/contents/laparoscopic-roux-en-y-gastric-bypass
Mechanick, J. I., Apovian, C., Brethauer, S., Garvey, W. T., Joffe, A. M., Kim, J., Kushner, R. F., Lindquist, R., Ressah-Pollack, R., Seger, J., Urman, R. D., Adams, S., Cleek, J. B., Correa, R., Figaro, M. K., Flanders, K., Grams, J., Hurley, D. L., Kothari, S., . . . Still, C. D. (2020). Clinical practice guidelines for the perioperative nutrition, metabolic, and nonsurgical support of patients undergoing bariatric procedures—2019 update: Cosponsored by American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists/American College of Endocrinology, The Obesity Society, American Society for Metabolic & Bariatric Surgery, Obesity Medicine Association, and American Society of Anesthesiologists. Surgery for Obesity and Related Diseases, 16(2020), 175–247. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soard.2019.10.025
Mitchell, B. G., Collier, S. A., & Gupta, N. (2024). Roux-en-Y gastric bypass. StatPearls [Internet]. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK553157
National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. (2020a). Types of weight-loss surgery. US Department of Health and Human Services. https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/weight-management/bariatric-surgery/types
National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. (2020b). Weight-loss surgery benefits. https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/weight-management/bariatric-surgery/benefits
National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. (2020c). Weight-loss surgery side effects. https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/weight-management/bariatric-surgery/side-effects
Office of Disease Prevention and Health Promotion. (n.d.). Reduce the proportion of adults with obesity—NWS-03. Healthy People 2030. Retrieved June 26, 2025, from https://odphp.health.gov/healthypeople/objectives-and-data/browse-objectives/overweight-and-obesity/reduce-proportion-adults-obesity-nws-03
Olson, E. J., Chung, F., & Seet, E. C. P. (2025). Surgical risk and the preoperative evaluation and management of adults with obstructive sleep apnea. UpToDate. Retrieved June 29, 2025, from https://www.uptodate.com/contents/surgical-risk-and-the-preoperative-evaluation-and-management-of-adults-with-obstructive-sleep-apnea
Panuganti, K. K., Nguyen, M., & Kshirsagar, R. K. (2023). Obesity. StatPearls [Internet]. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK459357
Rosenthal, R. J., Szomstein, S., & Lo Menzo, E. (2024). Laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy. StatPearls [Internet]. Retrieved June 28, 2025, from https://www.uptodate.com/contents/laparoscopic-sleeve-gastrectomy
Sall, A. R., & Jones, M. W. (2023). Bariatric surgery preoperative assessment. StatPearls [Internet]. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK594256
Seelbach, C. L., & D’Almeida, M. J. (2022). Postoperative assessment and management of obesity surgery. StatPearls [Internet]. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK563131
Seeras, K., Acho, R. J., & Prakash, S. (2023). Laparoscopic gastric band placement. StatPearls [Internet]. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK526062
Seeras, K., Sankararaman, S., & Lopez, P. P. (2023). Sleeve gastrectomy. StatPearls [Internet]. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK519035
Skelton, J. A., & Klish, W. J. (2025). Definition, epidemiology, and etiology of obesity in children and adolescents. UpToDate. Retrieved June 30, 2025, from https://www.uptodate.com/contents/definition-epidemiology-and-etiology-of-obesity-in-children-and-adolescents
Stahl, J. M., & Malhotra, S. (2023). Obesity surgery indications and contraindications. StatPearls [Internet]. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK513285
Telem, D., Greenstein, A. J., & Wolfe, B. (2025). Outcomes of bariatric surgery. UpToDate. Retrieved June 29, 2025, from https://www.uptodate.com/contents/outcomes-of-bariatric-surgery
World Health Organization. (2021). Obesity. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/obesity-and-overweight
World Health Organization. (2025). Obesity and overweight. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/obesity-and-overweight
World Obesity. (2024). Ranking (% obesity by country). Global Obesity Observatory. https://data.worldobesity.org/tables/ranking-obesity-by-country-adults-1.pdf
Powered by Froala Editor